Why can’t electric cars charge themselves? Below will give you the top 9 reasons, the available technologies for an electric car to charge itself, and how would a self-charging electric car work.
Why can’t electric cars charge themselves? Inadequate solar energy conversion goes without an engine, lack of alternators, faulty wiring or bad connections, lack of charging stations, electric vehicle battery shortage, insufficient electricity, battery maintenance, and technology doesn’t exist yet.
Continue reading for more information.
Why Can’t Electric Cars Charge Themselves?
Why can’t electric cars charge themselves? That query and the reasons why electric cars cannot operate autonomously are addressed in this article.
Inadequate Solar Energy Conversion
Since electric vehicles are the new environmentally friendly choice, they are powered by batteries that can be recharged in a variety of ways, such as using solar power or the electrical grid.
With, a solar car is an electric automobile that collects all or a significant portion of its energy from the sun.
Additionally, photovoltaic cells, which turn solar energy directly into electricity, are a common component of solar panels.
Energy transformations are not entirely efficient because some energy is lost as heat while being converted.
Electric vehicles are unable to recharge because of energy loss as a result.

Goes Without Engine
Tesla is one top brand of electric vehicles. However, since Tesla vehicles lack engines, they only use electric motors with rechargeable batteries as opposed to other propulsion.
Electric motors with rechargeable batteries are used to propel it. In essence, each of these motors only drives one axle.
That said, to recharge an electric car without an engine, you must plug it into an outlet or connect it to a wall socket using a charging cable.
However, an electric car lacks the source of power that an engine does, making it unable to charge on its own. An engine uses gasoline to generate power that can be used to move a vehicle.
Read about: Can You Charge a Tesla in the Rain?
Lack of Alternators
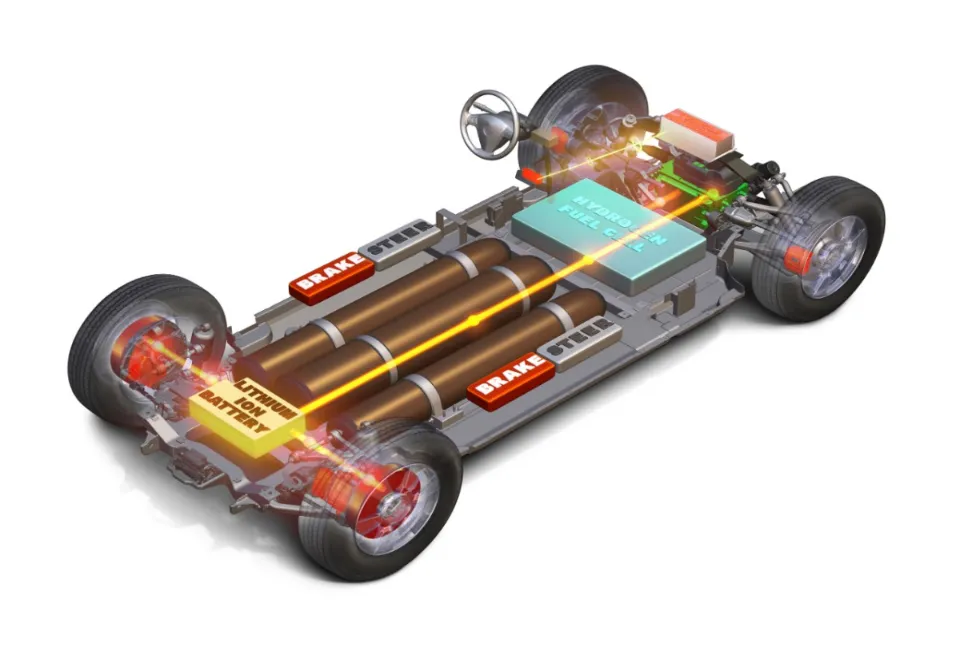
One of the biggest reasons electric cars won’t charge themselves is the lack of alternators. The alternator, then, is what transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy.
In addition, lithium-ion batteries, which are considerably smaller than the conventional batteries used in cars today, power the majority of electric vehicles.
Electric cars lack an alternator and instead rely on a DC-to-DC converter to recharge the 12-volt battery with power from the high-voltage battery that powers the motor.
Your vehicle won’t be able to recharge itself without one.

Faulty Wiring Or Bad Connections
The charging port and the battery are the two main parts that are connected to the plug when you plug in your car. While connected, the battery charges, but a proper network setup is required.
Your electric car won’t be able to recharge on its own if the charging port is malfunctioning or the cables are improperly connected or damaged.
Therefore, even though three-pin plug sockets can be used to charge electric vehicles, they are not designed to withstand the heavy loads that EVs require for an extended period of time.
Therefore, if you have an electric vehicle with a faulty wire or connection, it will prevent your car from charging.
Lack of Charging Stations
Forbes claims that the absence of EV charging stations could slow EV growth. This is due, in part, to a lack of available charging stations for all-electric vehicles.
Therefore, if they lack access to public charging stations, these potential customers may never be able to appreciate what a great investment an electric car is.
As a result, the shortage of charging stations makes it difficult for drivers to accept and utilize them because they may have to travel a long distance or spend the night to get to one.
For electric vehicles to be able to charge themselves, they need more charging stations.

Electric Vehicle Battery Shortage
Although EVs are becoming popular, Stellantis CEO Carlos Tavares predicted shortages of the batteries and raw materials required to produce electric vehicles in the upcoming years.
While some new technologies on the market could make it more practical for batteries to last longer, there are still plenty of limitations to be overcome before everyone can charge cars daily.
To store enough energy to travel long distances, electric vehicles also require a large battery capacity.
In addition, due to a scarcity of supplies, consumers cannot charge their electric vehicles.
Read about: Are There Mercedes-Benz Hybrid Models?
Insufficient Electricity
California energy officials warned people to prepare for possible blackouts in the summer as the state’s energy grid faces capacity issues.
The state also agreed to phase out all gas-powered vehicles by 2035, so the additional load from EV charging could put more strain on the electric grid.
Through the extensive electric system, electricity is provided to millions of homes and businesses.
However, if too many cars attempted to charge themselves, the grid would be put under additional stress, which could result in a decrease in power supply.
Essentially, people won’t be able to charge their cars if there isn’t enough electricity since they won’t have adequate power.

Battery Maintenance
Batteries can malfunction for a variety of reasons, including corrosion, insufficient charging, and prolonged high heat.
Weather, temperature changes, and even how frequently you charge your car can all have an impact on battery life.
It may be impossible for your battery to hold a charge or even to start up at all if it isn’t functioning properly.
Additionally, if you want your electric cars to begin charging themselves, keep this in mind and first check the health of your battery.
Technology Doesn’t Exist Yet
Lack of infrastructure to support self-charging vehicles is one of the biggest issues businesses working on electric vehicles encounter.
Additionally, there is no government support for self-charging cars, and there are no regulations or standards for such things.
Without regulations or standards, building a mass-produced electric car that can charge itself is nearly impossible.

The Available Technologies for An Electric Car to Charge Itself
The technologies that are currently available that an electric car could use to recharge itself will be discussed next. The fee for using those technologies, however, will only be a portion of what was previously stated.
Regenerative Braking
For example, the Tesla Model S is using a simple transmission and a clever regenerative braking system that can turn its electric motor into a generator when the car is decelerating. This means that when you lift your foot from the pedal the car will slow down not just because you are cutting the power to the motor. In fact, the motor will begin functioning as a generator at that point and turn kinetic energy back into electricity.
A similar system but with different mechanisms can also be installed on standard internal combustion engine cars. This is the kinetic energy recovery system (KERS) and is a unique type of braking system that converts the kinetic energy of the car back into electricity while the car is breaking.
Formula 1 teams have put a lot of effort into developing and researching regenerative braking systems. This is a nice example of how motorsport can be used to promote research on technologies that help environmental sustainability.
Either way, the recovered electricity is then stored in electric car batteries and used when needed.
Regenerative braking only functions when the car decelerates or needs to brake frequently, such as in urban areas, because it uses kinetic energy while the vehicle is breaking or decelerating.
Regenerative driving is majorly considered a form of self-charging and is currently used by hybrid cars. However, while it may count as a form of self-charging, it is not effective enough to charge an electric car fully. Because of this, the special type of breaking only manages to capture a small amount of energy, which is insufficient to allow the electric car to fully recharge.
Solar Panels
Simply put, solar panels won’t produce enough power to charge an electric vehicle, which is the main reason they are typically not installed on electric vehicles.
Just visualize for a minute the size of your electric car. I don’t think it has a very big roof, do you? In order to move, an electric car must simultaneously store a lot of energy. Its numerous batteries are a result of this.
Additionally, the power generated by solar panels mounted on top of the electric car would only be sufficient to run a few small systems.

Ongoing Research and Prototypes
The creators claim that a fully charged battery will enable this solar-powered car to travel up to 388 miles. Even better, the solar panels can increase the car’s on-the-road range by as much as 70 miles!
And as for the cost of the vehicles, one Lightyear 0 car sold for more than $200,000.
How Would a Self-Charging Electric Car Work?
Several theories have been proposed by researchers as to how an electric car might one day charge itself.
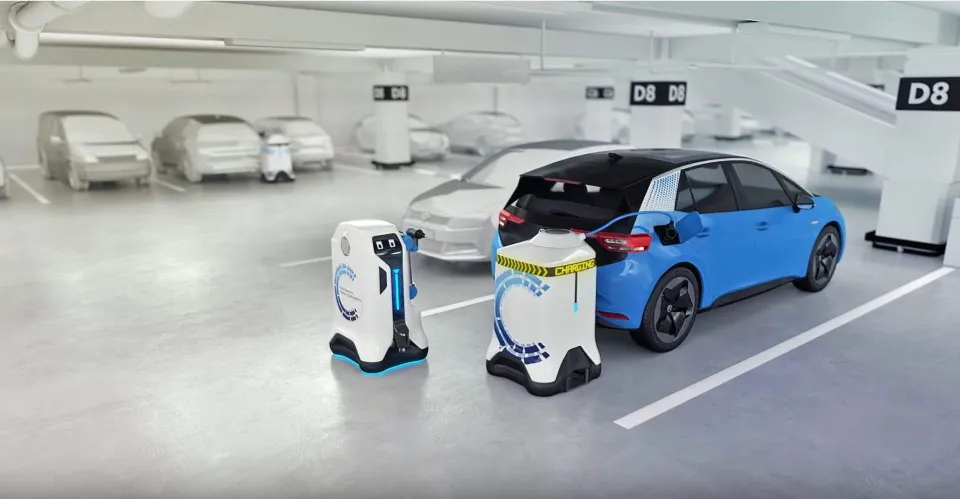
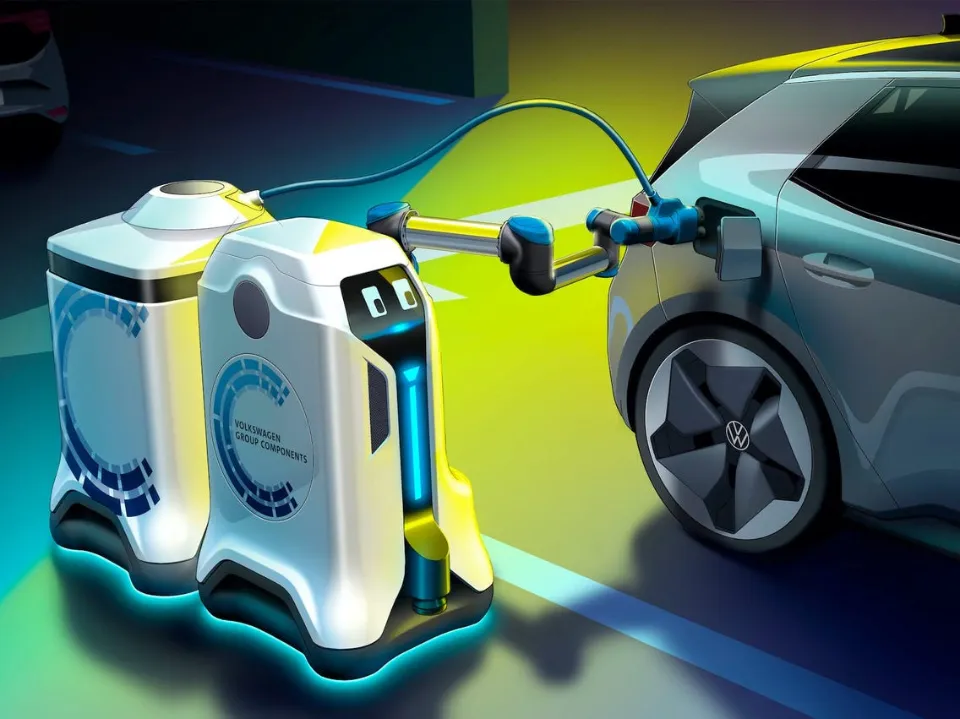
Volkswagen Autonomous Charging Robots
This research was proposed by the Volkswagen (2019 saw the formation of the Volkswagen (VW) group, and they developed the idea of having mobile charging robots that can communicate with electric vehicles. These robots would be controlled by the drivers through an app. Additionally, they would be put in parking lots so that people could use them as needed to charge their cars.
Although the concept of autonomous charging robots for Volkswagen is still in its infancy, the VW group is making a lot of effort to promote it.
The concept, however, raises serious technological and infrastructural challenges, so it is unlikely to become a reality anytime soon.

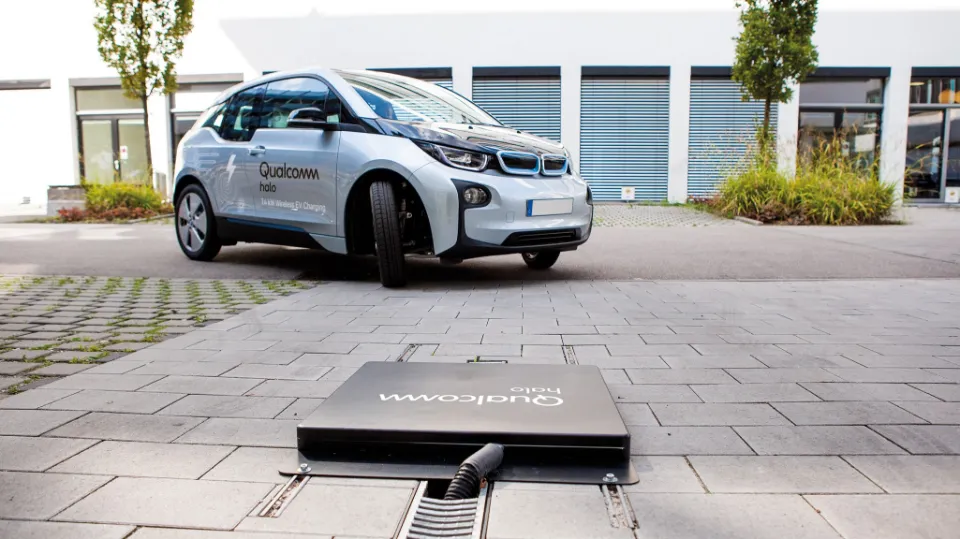
Wireless Charging
Electromagnetic induction is used for wireless charging. Typically, an electric current is first detected and then stored in a battery. It is then transmitted using two coils, one of which is located on the electric car and serves as the receiver, and the other of which is housed in the charging unit and serves as the transmitter.
A wireless charger would be installed on the road or in the garage to efficiently charge electric vehicles.
However, since this is a high-end type of technology, it will most likely take a long to be actualized. Still, there is hope that this will be possible because there are already some products that use this mechanism to charge an electric vehicle.
By the way, this is just a shortcut for charging an electric vehicle without manually inserting the power plug.

Alternators Connected to the Wheels
The electric vehicle’s wheels are each fitted with an alternator as part of this self-charging technique.
Although this technology might replace the KERS, it won’t be able to supply enough power to completely charge the vehicle.
This is, again, because part of the energy will be dissipated by the heat due to the friction between moving parts.
In essence, any device that tries to harness the energy of the car’s motion can only do so partially. There is no getting around this because it is a result of the fundamental laws of physics.

Will We See More Self-Charging Electric Cars in the Future?
Future self-charging electric vehicles are likely to be more prevalent due to the technology’s rapid advancement. Politics and science remain obstacles that must be surmounted, though.
- Science
The scientific theories we discussed above are not very useful. Therefore, there are still a lot of challenges to be solved. For example, solar power doesn’t charge a car very fast and generators aren’t effective because they can’t capture all the kinetic energy. The wind turbine theory has the most serious flaws.
This is fundamentally flawed because wind turbines would weigh too much and produce excessive drag. The car will slow down as a result, requiring more energy just to start moving. A “vicious circle” would be created if more wind turbines were added as a solution to this problem.
But new discoveries in science appear every day. While there are no viable options for a self-charging electric car in March 2022, that doesn’t mean that the picture won’t have completely changed within the next couple of years.

- Politics
Simply put, no government is funding the purchase of electric vehicles that can recharge on their own. Nobody is yet willing to provide them with the strong political backing and investment they will need to move forward. This is primarily because electric cars may have negative environmental effects.
More importantly, there are huge infrastructure issues. Self-charging automobiles are not currently supported by our society, and the logistics to make that transition are difficult and involved.
We won’t see any more in the near future unless these mentalities shift and we make the significant strides required to make self-charging cars practical and affordable.

FAQs
Isn’t Regenerative Braking a Form of Self-Charging?
Yes, regenerative braking technically counts as self-charging. However, it is nowhere near effective enough to fully recharge an electric car.
Regenerative braking depends on drivers depressing the brake pedal or lifting their foot off the accelerator frequently enough to collect kinetic energy and store it in the battery. Regenerative braking can greatly increase the range of your car if you frequently drive in cities or at low speeds. On the other hand, it is much more difficult to increase the range of your EV if you typically drive on the freeway.
Most importantly, regenerative braking only absorbs a portion of the energy. It is insufficiently efficient to produce a true self-charging car.
Why Don’t More Electric Cars Have Solar Panels to Charge Themselves?
Even though the Lightyear EV shows that a self-charging EV can be made from solar panels, there are still a number of problems with the technology.
It is very untested. Though it has undergone extensive testing, the Lightyear One has not yet been made available. Therefore, it is still unknown how long a solar-powered self-charging car will last.
The charging process takes a while for the car. According to Lightyear, for every hour of charging, their solar panels will extend your range by 12 km (7 miles). If you only travel short distances, this is beneficial. If you drive a long distance every day, however, it is not as helpful.
Right now, it’s very pricey. Prices for the Lightyear 0 are anticipated to begin at 297,500 euros (or 249,394.77 pounds). Although it’s still a ways off, there are plans for a Lightyear Two model that will be significantly less expensive.
The technology has only received investment from one company. One and only solar-powered, self-charging EV is the Lightyear 0. Furthermore, Lightyear is still a start-up and needs funding from outside sources just to get the car on the market.
As a result, fewer than 1,000 Lightyear 0 models will be made. So, while a solar-powered self-charging car is possible, they won’t be common for years to come.
Summary: Why Can’t Electric Cars Charge Themselves?
Your perplexity is entirely understandable! Electric cars can’t charge themselves because some of the energy is lost. Energy conversions aren’t 100% efficient because some of the energy dissipates during the conversion process in the form of heat.
However, your car recycles some energy through regenerative braking. Regenerative braking converts an electric vehicle’s kinetic energy into a form that is useable for the car’s battery.
KV Auto tries to give you the best car industry information. If you have any questions, please leave a comment. Don’t forget to share the post. Thank you for reading.





