We’ll examine the four main types of hybrid vehicles in this article and discuss what makes each one distinctive. They are Mild Hybrids, Full Hybrids, Plug-In Hybrids, and Electric Vehicles with Range Extender Hybrids. Continue reading.
What is a Hybrid Car?
A car that uses multiple power sources, each of which is operated independently, is referred to as a hybrid.” The majority of the time, this refers to a gas engine and an electric motor. A battery pack that aids the gas engine in accelerating also powers the electric motor. This enhances fuel economy.
Here is a quick look at Hybrid Vs Gas Car. A gas-powered car only has a traditional gas engine, while a hybrid vehicle also has an electric motor. Since hybrid vehicles can switch between their gas and electric motors while being driven, they typically have higher fuel efficiency than their gasoline-powered counterparts.
Types of Hybrid Cars
Here the details about types of hybrid cars:
Mild Hybrids
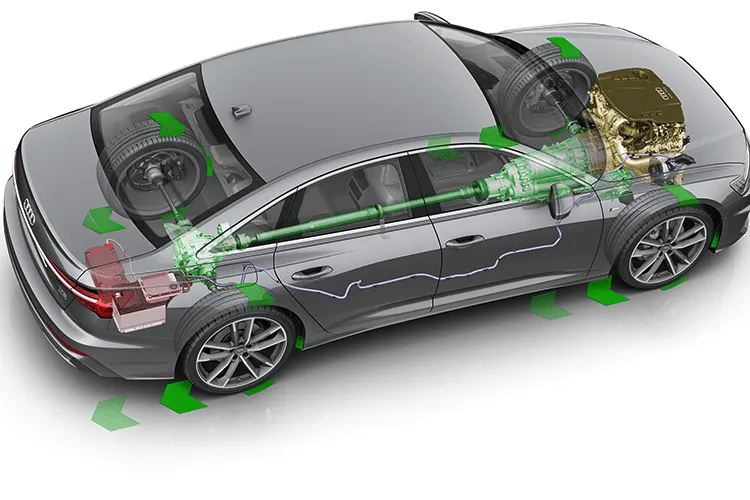
There is a renaissance of sorts for the mild hybrid electric vehicle (MHEV). It’s possible that you’ve driven a mild hybrid vehicle without realizing it because many vehicles use MHEV powertrains without promoting them as such.
The mild hybrids depend on their internal combustion engines the most out of all the different types of hybrid cars. The electric motor can engage when coasting, braking, or cruising, but the engine typically handles the majority of the work. The engine and motor work together to help you accelerate after it gives you the initial burst of power to get off the starting line.
The full hybrid electric vehicle, the next hybrid on our list, is more economical than a MHEV, though it may be slightly more fuel-efficient than an all-gasoline vehicle.
Editor’s Advice: How Much Does a Hybrid Battery Cost? Compared to conventional gasoline-only vehicles, hybrids use different batteries, and their prices range from $1,000 to $8,000. The final cost you’ll incur is determined by the make and model of your car as well as whether you choose a new or refurbished battery.
Full Hybrids

Full hybrid vehicles are similar to mild hybrids in that they have an electrical component in addition to a gasoline engine. A full hybrid vehicle’s electrical system, in contrast, can manage a much higher workload than a mild hybrid. The majority of full hybrids can actually travel a certain distance using only electric power. This typically occurs at lower city speeds, which is one reason why the city MPG rating of a full hybrid may be higher than the highway MPG rating (whereas the opposite is true for standard gasoline-powered vehicles).
There are two main categories of powertrains for full hybrid cars: parallel hybrids and series hybrids.
In parallel hybrids, the engine can be powered in one of three ways: directly by the engine, directly by the electrical motor, or by both systems working together.
In a Series hybrid, the gasoline engine functions as a sort of generator for the electric motor, which powers the wheels exclusively. Never actually driving the wheels is the gasoline engine.
With advances in hybrid technology, some vehicles operate as a combination of the two (aptly named “series-parallel” hybrids), with the on-board computer system choosing the most efficient way to operate at any given time.
Similar to mild hybrid systems, full hybrids use both regenerative braking and energy from the gasoline engine to power their battery systems.
Editor’s tip: Just like with all cars, your Prius’ battery will eventually need to be replaced. But when will that be? How long do Toyota Prius batteries last?
Plug-In Hybrids

All of the hybrid vehicles that we have discussed so far only use internal energy to recharge their batteries. The primary distinction between plug-in hybrids and other vehicles is that the batteries in these models can be charged both internally and externally. Therefore, compared to full hybrids, plug-in hybrids typically have longer electric-only driving ranges. In a sense, plug-in hybrids act as a transitional type of vehicle between full hybrid and all-electric models. Question: What are Hybrids Vs. Plug-in Hybrids, and how do the two types of vehicle compare? (Related: How Long Do Hybrid Car Batteries Last? About 100,000 miles should be covered by the majority of hybrid batteries. Some owners are able to increase this number to 200,000 with excellent maintenance.)
Electric Vehicles With Range Extender Hybrids
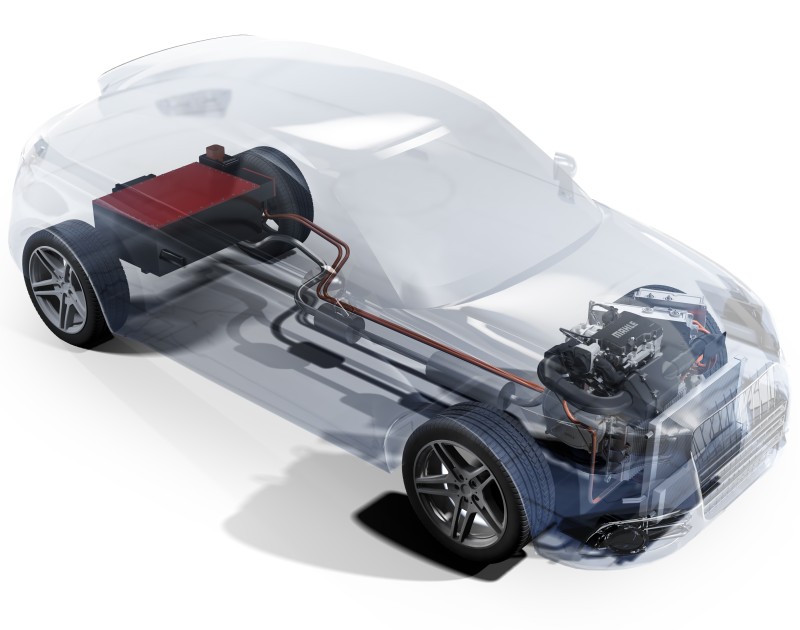

Despite the fact that all-electric cars aren’t considered hybrids, some do have a small gasoline engine to help out when necessary. An electric vehicle will require charging after it runs out of power in order to resume operation. In order to keep you from becoming stranded, these hybrid range extenders use their gasoline engine to either charge the battery or power the electric motor. This can mean anywhere between a few dozen miles and hundreds of miles, depending on the size of the gasoline engine. (Are hybrid cars good for long distance driving? How far a typical hybrid can travel will be covered in this blog.)
Suggested reading: Thankfully, the market for used hybrids is rich enough for us to pick and choose those with the highest safety and reliability ratings, plus low overall cost of ownership. The best used hybrid cars are those listed here.
Benefits of Owning a Hybrid Car
Owning a hybrid car has a lot of advantages, including better fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and tax breaks.
Typically, full hybrids can increase fuel economy by up to 30%, compared to mild hybrids’ up to 10% improvement. PHEVs can go further on electric power alone, using even less gasoline.
In comparison to conventional gasoline vehicles, hybrid vehicles have lower emissions. This is so that they can use electricity, which has no emissions. Additionally, hybrid vehicles’ smaller engines result in lower emissions.
Tax breaks and other incentives are available for many hybrid vehicles. The federal government offers a tax credit of up to $7,500 for certain hybrid and electric vehicles. Some states also provide discounts on registration fees and access to HOV lanes.
Read about





